Page 14 • (167 results in 0.045 seconds)
-
claim that to truly exemplify what it is to perform, is to incorporate the process of evolution into the art. One character that is often represented in the masks is a pregnant female. In this case, in addition to the female lipiko, a male dancer will wear a full body mask, called the Anwalindembo, representing a pregnant stomach. During a performance with these masks the dancer dramatizes the agonies of childbirth. The dance not only celebrates the initiation of young women into adulthood, it also
-
claim that to truly exemplify what it is to perform, is to incorporate the process of evolution into the art. One character that is often represented in the masks is a pregnant female. In this case, in addition to the female lipiko, a male dancer will wear a full body mask, called the Anwalindembo, representing a pregnant stomach. During a performance with these masks the dancer dramatizes the agonies of childbirth. The dance not only celebrates the initiation of young women into adulthood, it also
-
claim that to truly exemplify what it is to perform, is to incorporate the process of evolution into the art. One character that is often represented in the masks is a pregnant female. In this case, in addition to the female lipiko, a male dancer will wear a full body mask, called the Anwalindembo, representing a pregnant stomach. During a performance with these masks the dancer dramatizes the agonies of childbirth. The dance not only celebrates the initiation of young women into adulthood, it also
-
claim that to truly exemplify what it is to perform, is to incorporate the process of evolution into the art. One character that is often represented in the masks is a pregnant female. In this case, in addition to the female lipiko, a male dancer will wear a full body mask, called the Anwalindembo, representing a pregnant stomach. During a performance with these masks the dancer dramatizes the agonies of childbirth. The dance not only celebrates the initiation of young women into adulthood, it also
-
claim that to truly exemplify what it is to perform, is to incorporate the process of evolution into the art. One character that is often represented in the masks is a pregnant female. In this case, in addition to the female lipiko, a male dancer will wear a full body mask, called the Anwalindembo, representing a pregnant stomach. During a performance with these masks the dancer dramatizes the agonies of childbirth. The dance not only celebrates the initiation of young women into adulthood, it also
-

learned. “The human story is a very complex thing,” he said. “History doesn’t start and then stop. It’s more of an evolution.” As for his study of religion, Jones saw it as a catalyst for the history he was studying and wanted to know more. “Religion provides a huge worldview,” he said. “When you understand the religion, history makes a whole lot more sense.” Jones’ intersecting identities have evolved since graduation. He came out as trans in July 2017 and changed his name. “PLU is awesome in that
-
forward in his chair to talk about what he’s learned. “The human story is a very complex thing,” he said. “History doesn’t start and then stop. It’s more of an evolution.” As for his study of religion, Jones saw it as a catalyst for the history he was studying and wanted to know more. “Religion provides a huge worldview,” he said. “When you understand the religion, history makes a whole lot more sense.” Jones’ intersecting identities have evolved since graduation. He came out as trans in July 2017 and
-

normally see in the community very often,” Larsen said. Adequate medical care for inmates is a constitutional right. But for Larsen, it’s more than that. “I get a direct, daily sense that I make a difference,” he said. “What I do now is right in front of me, it’s almost immediate all the time.” And that feeling was precisely what Larsen was after when he made a midlife career change more than a decade ago. Larsen, who studied evolution and avian ecology at The Evergreen State College, worked as a
-
surface with emphasis on the effects of rock type, geologic structure, and climate on the formation and evolution of landforms. Includes labs. Prerequisite: ESCI 201 or consent of instructor. (4) ESCI 336 : Geochemistry Study of fundamental geochemistry principles with focus on applications to investigations into a wide-range of earth and atmospheric processes and systems. Analysis and interpretation of student-collected and published field and lab data. Includes labs. Prerequisite: ESCI 201 and
-
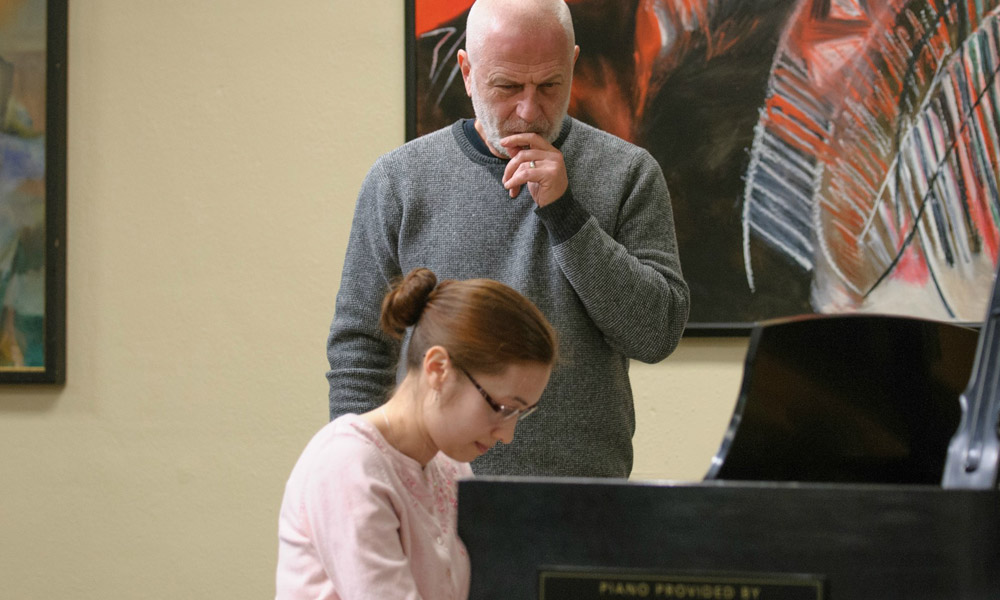

piano—that is a lifelong gift. I am also interested in continuing research on my senior project, called “The Evolution of Piano Pedagogy and Culture in China.” What are your other plans and hopes for the future? Besides using piano and Chinese proficiently in a career, I don’t have many plans. I always hope to love God and people better with whatever I’m doing, though. How did a PLU education prepare you for the real world? Was anyone here particularly influential in your life or career plans? There
Do you have any feedback for us? If so, feel free to use our Feedback Form.