Page 4 • (624 results in 0.019 seconds)
-

Associate Professor | Department of Computer Science | caora@plu.edu | 253-535-7409 | My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein structure predictions.
Regulation Networks of Normal and Malignant Human Cell Types." PLoS ONE Vol. 8(3), 2013: e58793. Z. Wang, R. Cao, J. Cheng. "Three-Level Prediction of Protein Function by Combining Profile-Sequence Search, Profile-Profile Search, and Domain Co-occurrence Networks." BMC Bioinformatics Vol. 14(Suppl 3):S3, 2013: Biography My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein
Office HoursMon: 10:00 am - 2:00 pmMon - Fri: - -

Associate Professor of Computer Science | Innovation Studies | caora@plu.edu | 253-535-7409 | My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein structure predictions.
bioinformatics Vol. 16(1), 2015: 338. Biography My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein structure predictions. In addition, I am interested in promoting early engagement of undergraduate students (especially for women and underrepresented students) in machine learning, bioinformatics, and the data science field by interdisciplinary studies, and inspiring students
-
Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) graduate students will develop a broad understanding across biomedical disciplines with strong foundations in quantitative literacy and critical thinking. This allows our students to identify important biomedical questions, design and execute experimental approaches, conduct data analysis and interpretation, and…
Virtual Open House – Oregon Health and Science University Posted by: nicolacs / September 24, 2021 September 24, 2021 Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) graduate students will develop a broad understanding across biomedical disciplines with strong foundations in quantitative literacy and critical thinking. This allows our students to identify important biomedical questions, design and execute experimental approaches, conduct data analysis and interpretation, and communicate rigorous
-

Associate Professor of Computer Science | The PLU Chinese Studies Program | caora@plu.edu | 253-535-7409 | My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein structure predictions.
bioinformatics Vol. 16(1), 2015: 338. Biography My research interest is mainly focused on developing and applying machine learning and data mining techniques to solve biomedical problems, such as human genome data analysis and protein structure predictions. In addition, I am interested in promoting early engagement of undergraduate students (especially for women and underrepresented students) in machine learning, bioinformatics, and the data science field by interdisciplinary studies, and inspiring students
-
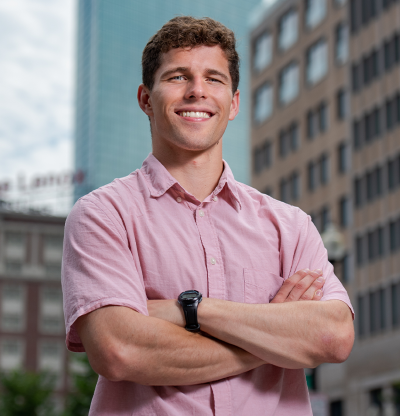

While this advice might sound cliché, people give it often, and for good reason. Just ask Pacific Lutheran University’s Keegan Dolan ’22. Dolan, a double major in philosophy and economics, is in the midst of a prestigious summer internship at the Analysis Group’s headquarters in…
How Keegan Dolan’s PLU Mentor Helped Land Him A Dream Internship In Boston Hard work pays off. Networking is key. Relationships are everything. Just ask PLU's Keegan Dolan '22. Posted by: tpotts / July 13, 2022 July 13, 2022 While this advice might sound cliché, people give it often, and for good reason. Just ask Pacific Lutheran University’s Keegan Dolan ’22. Dolan, a double major in philosophy and economics, is in the midst of a prestigious summer internship at the Analysis Group’s
-

Below are links to Mortvedt Library or open web materials by panelists and PLU faculty participating in the Wang Center 2022 symposium, HEALING: PATHWAYS FOR RESTORATION AND RENEWAL . Article: Healing, a Concept Analysis Firth, K., Smith, K., Sakallaris, B. R., Bellanti, D. M., Crawford,…
Mortvedt Library materials for HEALING: PATHWAYS FOR RESTORATION AND RENEWAL symposium Posted by: Holly Senn / February 16, 2022 February 16, 2022 Below are links to Mortvedt Library or open web materials by panelists and PLU faculty participating in the Wang Center 2022 symposium, HEALING: PATHWAYS FOR RESTORATION AND RENEWAL. Article: Healing, a Concept Analysis Firth, K., Smith, K., Sakallaris, B. R., Bellanti, D. M., Crawford, C., & Avant, K. C. (2015). Healing, a Concept Analysis. Global
-
The National Security Agency (NSA) has 3 summer opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students majoring in mathematics, statistics, and physics. Applications for summer 2022 are now open for the Directors Summer Program (DSP), Cryptanalysis and Signals Analysis Summer Program (CASASP), and Graduate Mathematics Program (GMP).…
Summer 2022 Internships at the National Security Agency Posted by: nicolacs / May 3, 2021 May 3, 2021 The National Security Agency (NSA) has 3 summer opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students majoring in mathematics, statistics, and physics. Applications for summer 2022 are now open for the Directors Summer Program (DSP), Cryptanalysis and Signals Analysis Summer Program (CASASP), and Graduate Mathematics Program (GMP). These 12 week paid internships provide students with the
-
The National Security Agency (NSA) has three exciting 2023 summer internship opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students majoring in mathematics, statistics, and physics. Applications for summer 2023 will open on 1 September 2022 for the Directors Summer Program, Cryptanalysis and Signals Analysis Summer Program, and…
Summer Internships at the National Security Agency Posted by: nicolacs / May 10, 2022 May 10, 2022 The National Security Agency (NSA) has three exciting 2023 summer internship opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students majoring in mathematics, statistics, and physics. Applications for summer 2023 will open on 1 September 2022 for the Directors Summer Program, Cryptanalysis and Signals Analysis Summer Program, and Graduate Mathematics Program. These 12 week paid internships provide
-
Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) graduate students will develop a broad understanding across biomedical disciplines with strong foundations in quantitative literacy and critical thinking. This allows our students to identify important biomedical questions, design and execute experimental approaches, conduct data analysis and interpretation, and…
Virtual Open House – Oregon Health and Science University Posted by: nicolacs / September 24, 2021 September 24, 2021 Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) graduate students will develop a broad understanding across biomedical disciplines with strong foundations in quantitative literacy and critical thinking. This allows our students to identify important biomedical questions, design and execute experimental approaches, conduct data analysis and interpretation, and communicate rigorous
-
Intellectual Ventures and TerraPower Innovation are seeking a Radiochemistry and Isotopes Intern. This paid internship position will participate in activities related to the chemistry of radioelements and their resulting compounds. The TerraPower laboratory has a range of characterization tools including; thermal gravimetric analysis/differential scanning calorimetry, powder…
Radiochemistry and Isotopes Intern Posted by: nicolacs / April 21, 2017 April 21, 2017 Intellectual Ventures and TerraPower Innovation are seeking a Radiochemistry and Isotopes Intern. This paid internship position will participate in activities related to the chemistry of radioelements and their resulting compounds. The TerraPower laboratory has a range of characterization tools including; thermal gravimetric analysis/differential scanning calorimetry, powder X-ray diffraction, inductively
Do you have any feedback for us? If so, feel free to use our Feedback Form.